MRI Anatomy: How It Helps in Early Detection of Brain Disorders
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has emerged as a critical tool in the early detection and diagnosis of brain disorders. By providing high-resolution images of the brain’s anatomy, MRI helps healthcare professionals identify abnormalities and changes that may not be detectable through physical symptoms alone. Early detection through MRI brain anatomy is essential for preventing further damage and improving treatment outcomes for patients. This article explores how MRI plays a key role in the early detection of various brain disorders.
Understanding MRI Brain Anatomy
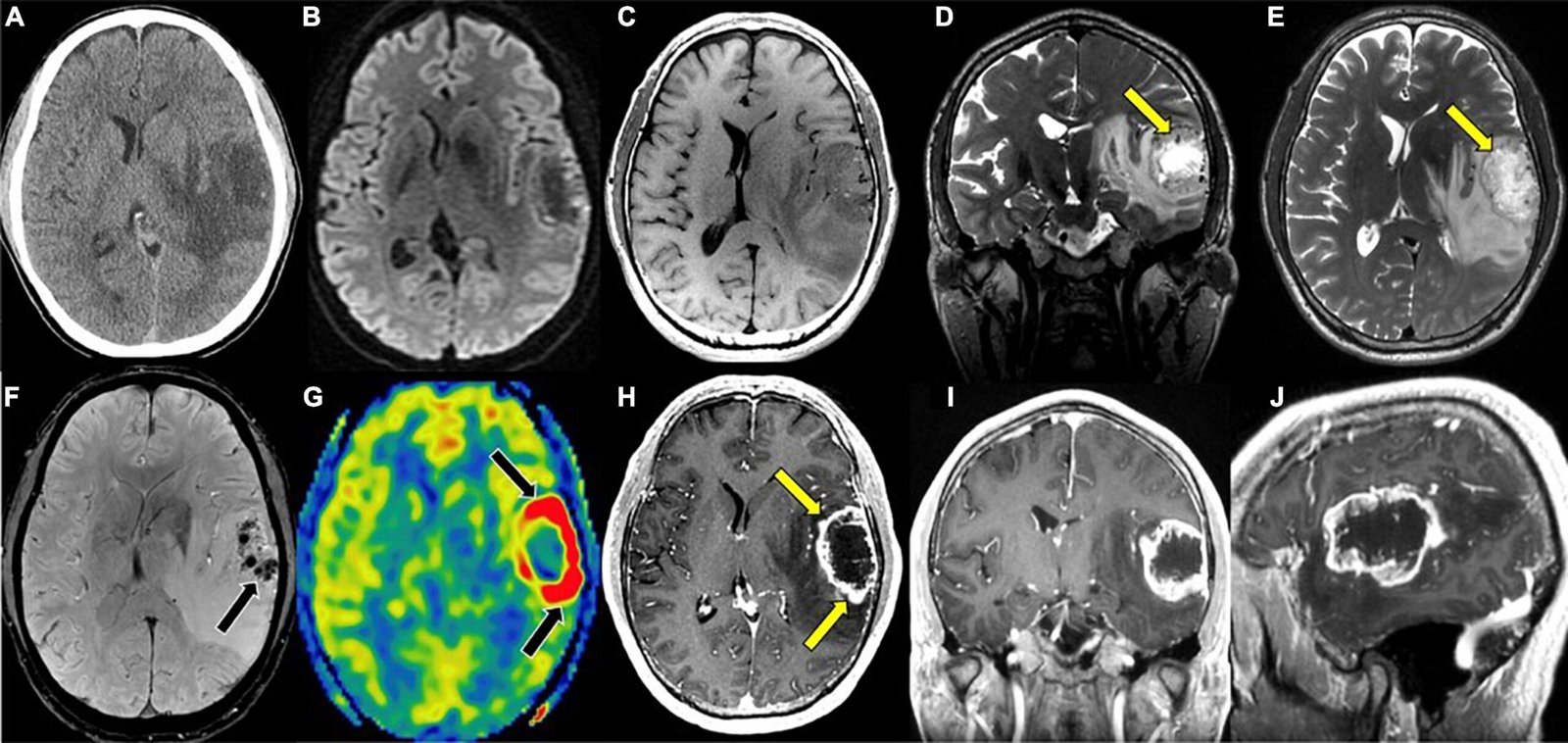
MRI brain anatomy refers to the process of obtaining detailed images of the brain’s internal structures using magnetic fields and radio waves. Unlike traditional imaging techniques such as X-rays or CT scans, MRI does not utilize ionizing radiation, making it a safer option, especially for patients requiring multiple scans. It produces high-resolution images that allow doctors to examine the brain’s gray and white matter, ventricles, blood vessels, and other critical structures. This comprehensive view aids in diagnosing a range of neurological disorders at their earliest stages.
Early Detection of Brain Disorders Using MRI
- Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia
Structural MRI scans can detect early signs of Alzheimer’s disease by identifying shrinkage (atrophy) in key regions of the brain, such as the hippocampus. Functional MRI (fMRI) also allows doctors to assess changes in brain activity, which may indicate the onset of dementia before clinical symptoms become apparent. Identifying these changes early on can help in monitoring disease progression and preparing effective management strategies. - Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is characterized by the gradual degeneration of specific areas in the brain, such as the basal ganglia. Early detection through MRI, particularly using resting-state fMRI, can reveal disruptions in the connectivity of these brain regions. By identifying these early changes, doctors can intervene sooner, potentially slowing disease progression and improving the quality of life for patients. - Brain Tumors
MRI plays a crucial role in detecting brain tumors at an early stage. The high-resolution imaging allows for detailed visualization of the size, location, and type of tumor. Early detection is essential for developing the most effective treatment plan, whether surgical, radiation-based, or pharmacological. - Stroke
MRI is highly effective in identifying strokes at their earliest stages. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) detects changes in the movement of water molecules in brain tissue, which are typically affected during a stroke. This allows for immediate diagnosis and timely intervention, which is critical in minimizing long-term damage and improving recovery outcomes. - Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
MRI is the gold standard in diagnosing multiple sclerosis, a disease characterized by lesions in the brain and spinal cord. MRI can detect these lesions early, even before symptoms become pronounced, enabling doctors to begin treatment at an earlier stage and potentially delay the disease’s progression.
Advanced MRI Techniques for Early Diagnosis
Several advanced MRI techniques enhance its ability to detect brain disorders early on:
- Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI): This technique maps the orientation and integrity of white matter fibers in the brain. It is particularly useful for assessing conditions like multiple sclerosis, traumatic brain injury, and other disorders that affect the brain’s neural pathways.
- Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS): MRS analyzes the chemical composition of brain tissue, offering insights into the metabolic changes that may occur in various neurological disorders. This technique can detect early biochemical changes associated with conditions such as tumors, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s disease.
- High-Definition Fiber Tracking (HDFT): HDFT allows doctors to visualize neural connections in the brain, providing valuable information about brain connectivity. It is particularly useful for assessing the impact of disorders like traumatic brain injury or neurodegenerative diseases.
Benefits of Early Detection with MRI
- Improved Treatment Outcomes: Early detection of brain disorders through MRI allows for more effective and timely intervention. This can significantly improve treatment outcomes by preventing further deterioration and enabling doctors to begin the most appropriate treatment protocols early on.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: MRI provides detailed anatomical images that can help healthcare providers develop personalized treatment plans. By understanding the exact location and extent of abnormalities in the brain, doctors can tailor treatments to the individual needs of each patient, improving their chances of recovery.
- Ongoing Monitoring: MRI is not only useful for initial diagnosis but also for monitoring disease progression over time. Regular MRI scans can help track changes in the brain, allowing healthcare professionals to assess the effectiveness of treatments and make necessary adjustments to the care plan.
Conclusion
MRI has become an indispensable tool in the early detection and diagnosis of brain disorders. The ability to visualize detailed brain anatomy allows healthcare professionals to detect abnormalities that may otherwise remain undetected until later stages, when treatment options may be less effective. By enabling early intervention, MRI plays a pivotal role in improving patient outcomes, enhancing the accuracy of diagnoses, and facilitating personalized treatment plans. As MRI technology continues to evolve, its role in the early detection and management of brain disorders will only continue to expand, offering hope for better diagnosis and care for patients worldwide.